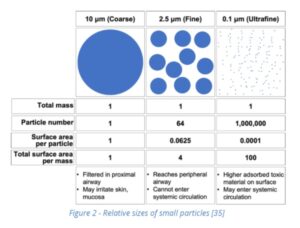
The current CAL-OSHA and federal OSHA standard that requires wet-cutting methods, exhaust ventilation, and dust masks, half-face canister respirators, and full-face canister respirators when fabricating natural stone was based on the low content of silica particles found in natural stone that are sized in the low micron range, and not the high volume of ultrafine or nanosized silica particles contained in artificial stone. As a result, the current OSHA standard does not provide adequate protection for the massive numbers of ultrafine and nanosized crystalline silica particles to which fabricators are exposed. For an analysis of the toxicological characteristics of artificial stone such as high concentration, ultrafine particles, irregular shapes, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and free radicals that cause severe silicosis see Why are the Particles Generated By Artificial Stone More Toxic Than Particles Generated By Natural Stone? – July 20, 2023 by Michael Wilson, PhD, MPH, CIH at CAL-OSHA.



Required Respiratory Protection for Artificial Stone Fabrication Workers
- Working without a mask does not prevent disease.
- N-95 masks do not prevent disease.
- A half or full-face elastomeric OV (organic vapor)/P-100 cartridge filter respirator will reduce, but not prevent disease. Also, note that the cartridge/filters must be regularly replaced.
- A Powered Air Purifying Respirator (PAPR) with an APF (Assigned Protection Factor) of 25/1000, if consistently used on conjunction with wet-equipment and no compressed air, should prevent most disease.
- Supplied air respirators (SAR) with an APF (Assigned Protection Factor) of 1000, if consistently used on conjunction with wet-equipment and no compressed air, will prevent most disease.


Video Credit: SHES at Georgia Tech
Studies have shown that workers in artificial stone fabrication shops are exposed to an average of 227 ug/m3, which is 4.5 times the OSHA Permitter Exposure Limit (PEL) for silica and 9 times the OSHA action level. With no controls, exposures ranged up to 2300 ug/m3, which is 46 times the PEL. Even when OSHA control methods were used, exposures ranged up to 360 ug/m3. Stated differently, water and exhaust ventilation do not reduce silica exposures below the OSHA silica PEL. Therefore, the only methods capable of fully preventing disease are a full air-fed positive pressure respirators, or a ban on the manufacture and sale of artificial stone.



According to the WHO (World Health Organization), there is no safe level of exposure to silica dust: “it cannot be assumed that there is a threshold at which exposure to silica would not result in silicosis and/or lung cancer.”
There are four primary methods of worker exposure to silica from artificial stone fabrication: direct within their immediate breathing zone, bystander from nearby workers, secondary exposure from resuspension or reentrainment of settled dust, and secondary exposure from inhalation of water particles containing dust.
While not as effective at disease prevention as an air fed positive pressure respirator or a complete ban, the CDPH (California Department of Public Health) – Occupational Health Branch maintains an updated website with Silica Safety Resources for Stone Fabricators and in Spanish at Fabricantes de Encimeras y Enfermedad Pulmonar. The CDPH site includes:
- Stone Fabrication Worker Hazard Alert and in Spanish at Alerta De Peligro Los Trabajadores, which can be printed and posted at work sites.
- Workplace Air Monitoring for Silica-Employer Guide and in Spanish at Monitorizacion En El Lugar De Trabajo De La Silice En El Aire.
- CAL/OSHA Silica Standard Overview and in Spanish at Vison General De La Norma De LA CAL/OSHA Sobre Silice.
- Hazard Warning: Silica Dust From Countertop Fabrication for employers.
- Hazard Warning: Silica Dust From Countertop Fabrication for workers, and in Spanish at Advertencia De Peligro: Polvo De Silice Generado Por El Trabajo En Encimeras, and in Chinese.
The California Labor Lab and the University of San Francisco maintain an updated California Artificial Stone and Silicosis Project.
Los Angeles residents who need free help signing up for Medi-Cal can contact Maternal and Child Health Access at (213) 749-4261.
The Texas Department of Health & Human Services – Silica Health Advisory maintains a worker health advisor – Worker Exposure to Silica Dust During Stone Countertop Fabrication – March 18, 2019
Georgia Tech’s Department of Safety, Health, & Environmental Services maintains training modules in English and Spanish for fabrication shop Control of Silica Exposure In Artificial Stone Fabrication Facilities
The U.S. Department of Labor – OSHA (Occupational Safety & Health Administration) has issued two respirable crystalline silica standards to protect workers.
OSHA and NIOSH have issued a Hazard Alert found at Worker Exposure to Silica during Countertop Manufacturing, Finishing, and Installation. Artificial stone fabrication workers have a right to a safe workplace. For information about OSHA worker rights and how to file a complaint with OSHA, see OSHA Worker Rights and Protections
The Western Occupational & Environmental Medical Association (WOEMA), has established the Silica Medical Exam Practitioner Roster, which is a list of medical facilities in California, Arizona, Utah, Nevada, and Hawaii which offer silicosis medical surveillance examinations for artificial stone workers.
State of California Department of Industrial Relations- California Adds Safeguards to Protect Workers Against Silicosis
Talk to An Attorney – No Cost Case Analysis
Engineered stone (Quartz) (artificial) (manufactured) countertop workers, who have been diagnosed with silicosis or lung cancer, or believe they may have silicosis, contact us online or call us at (855) 335-8606 for a no cost case analysis. You may be entitled to monetary recovery. Protect your rights.
For an overview of artificial stone, why it is dangerous, and how it causes silicosis and other diseases, click here
To learn about Safety and Medical resources, and how to reduce or eliminate exposure to silica, click here
To learn about what the manufacturers and distributors of artificial stone knew about the hazards of their products, click here
For an updated listing of current news, important regulatory hearings and medical presentations, and medical journal articles about the epidemic of artificial stone silicosis, click here
To learn about the types of monetary damages available to silicosis victims, statute of limitations (deadlines to file a lawsuit), or the major defendant manufacturers of artificial stone, click here










